Hyperautomation, also called Digital Process Automation (DPA) or Intelligent Process Automation (IPA), is a methodology that consists of expanding existing automation, such as production chains, workflows, and customer service processes, among others.
Essentially, it refers to the application of advanced artificial intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and RPA technologies, to automate processes that previously required human intervention, and even to create and adapt new automation.
It is a step beyond traditional automation, as it does not just focus on individual tasks or processes, but seeks end-to-end automation, meaning it addresses a broader range of jobs, tasks, and processes.
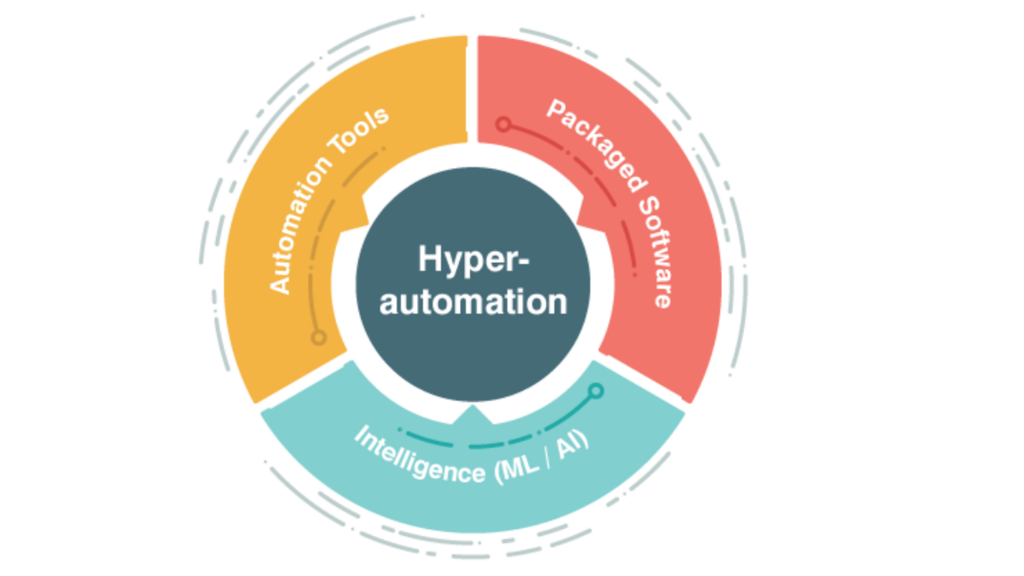
Elements Necessary for Hyperautomation
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) generally includes the following technologies and techniques:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): is a technology that automates high-volume, rule-based repetitive tasks previously performed by humans.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): This discipline allows machines to “think” like a humans and make decisions based on data.
- Machine learning (ML): A branch of AI that allows machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – Another branch of AI that allows machines to understand and interpret human language.
- Data Analysis: This process involves examining, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to discover useful insights, inform conclusions, and support decision-making.
It works by combining different technologies and techniques to automate, orchestrate, and optimize end-to-end business processes. In general terms this is how it works:
- Process Identification: The first step in Hyperautomation is to identify the processes that are suitable for automation. These can be time-consuming repetitive tasks, processes that require precision and accuracy, or processes that need to operate 24/7.
- Automation Development: Various technologies, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and natural language processing, are then used to create automation. These software development services can be used to perform tasks, make data-driven decisions, learn from data and improve over time, and interact in human language.
- Implementation and Orchestration: Once automations have been developed, they are implemented and integrated with other systems and processes. This often involves creating an “orchestration architecture,” which coordinates and manages the different automations.
- Monitoring and Optimization: After automation has been implemented, they are constantly monitored to ensure that they are working correctly and to identify opportunities for improvement. The data collected during this process can be used to improve and optimize automation.
6 Benefits of Hyperautomation in Companies
1. Increased efficiency and productivity:
Hyperautomation can carry out repetitive tasks more quickly and with fewer errors than humans, which can free up workers to focus on higher-value tasks.
Additionally, as Digital Process Automation (DPA) is developed and implemented, it is crucial to consider ethical and employment issues and look for ways to minimize job displacement and maximize social benefit.
2. 24/7 Operation:
Unlike humans, machines do not need to rest. This means they can continue working 24/7, which can be particularly useful for processes that need to operate continuously.
3. Cost reduction:
By increasing efficiency and productivity, Hyperautomation can help organizations reduce their operating costs.
A key aspect is that it is not just about replacing human tasks with machines, but rather using custom software development services to empower human workers, allowing them to focus on more complex and higher-value tasks.
4. Accuracy improvement:
Machines are less prone to errors than humans, especially in tasks that require a high level of precision and accuracy.
This can lead to better quality of work and greater customer satisfaction.
5. Large data capacity and analysis:
Hyperautomation can handle and analyze large amounts of data more efficiently than humans, which can allow organizations to obtain more accurate insights in less time.
6. Flexibility and scalability:
DPA solutions can be easily adapted or scaled to meet the changing needs of an organization.
Where can Hyperautomation have an impact?
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) can have a significant impact on a wide range of sectors. Here are some examples:
Health sector:
IPA systems can be used to schedule appointments, send medication reminders, automate patient data management tasks, perform medical image analysis, and more.
This can help improve efficiency and accuracy, free up time for patient care, and improve the overall quality of care.
Manufacturing:
In factories, Hyperautomation can be used to automate production and assembly tasks, quality control, predictive maintenance, and inventory management.
This can lead to greater efficiency, cost reduction, and better product quality.
Financial services:
Banks and financial institutions can employ DPA to automate processes such as customer background checks, transaction processing, fraud detection, and financial reporting, among others.
This can help improve efficiency, reduce the risk of human error, and improve customer experience.
Retail/E-commerce:
In retail and e-commerce, it can be used to automate processes such as inventory management, order processing, customer service, and personalizing the experience of the target audience.
Logistics and supply chain:
Hyperautomation can help automate and optimize processes such as route planning, inventory management, delivery tracking, and overall supply chain management.
Information technology:
In IT, IPA can be used to automate tasks such as incident management, system maintenance, network monitoring, and user problem resolution.
Public sector:
Governments and public organizations can employ Hyperautomation to improve the efficiency of their operations, from the management of citizen services to the implementation of policies and regulations.






